The CTO’s Dilemma: SaMD Is No Longer Optional
See Contents
- 1 The CTO’s Dilemma: SaMD Is No Longer Optional
- 2 The Illusion of Simplicity: Why SaMD Feels Manageable, Until It Isn’t
- 3 The Real Pain Points Keeping CTOs Up at Night
- 4 The Build vs Buy Trap in SaMD Decisions
- 5 Talent and Team Structure: You Can’t Just Hire Your Way Out
- 6 What the Smart CTOs Are Doing Differently
- 7 Conclusion: SaMD Isn’t Just Software. It’s Strategy
Today’s medical devices are no longer just about hardware. From wearables to diagnostic platforms, software is becoming the core of product innovation in healthcare. As a CTO, you’re expected to lead the transition toward Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), whether it’s enabling remote monitoring, AI-powered diagnostics, or patient engagement tools.
But with this opportunity comes a long list of risks.
And here’s the reality: you can’t ignore SaMD anymore. Healthcare is moving fast, and if your device isn’t software-enabled, you’re likely falling behind.
The assertion that “7 out of 10 Medical Device CTOs are losing sleep over SaMD” is strongly supported by industry data and expert insights.
A 2023 survey by the Deloitte Center for Health Solutions, which included 100 medtech leaders across the United States, Europe, and Asia, revealed that talent constraints are consistently ranked as a top barrier to digital transformation in software-driven devices (source).
Meanwhile, Sedgwick’s U.S. product recall index reported that medical device recalls saw a nearly 36% spike in Q3 of 2021, with software malfunctions being the leading cause in 21 of the last 22 quarters—a stark indicator of underlying development and compliance failures. (source)
On the regulatory front, analyses of FDA data show that up to 75% of first-time 510(k) or De Novo submissions for software-based devices require substantial revisions or face rejection, often due to missing risk files, traceability issues, or gaps relative to standards like IEC 62304 and ISO 14971. This feeds into the high stress CTOs feel when trying to meet both product and regulatory expectations.
On the workforce side, Deloitte finds that 62% of medtech service leaders cite talent gaps as a major concern, with nearly half of experienced field engineers set to retire within the next decade, creating a compound challenge in building SaMD-ready teams. (source)
Industry forums, webinars, and executive interviews further echo these pressures, CTOs express anxiety over shifting regulations, MVPs failing audits, and the constant conflict between speed and safety. Taken together, this combination of survey data, recall trends, regulatory hurdles, and talent shortages validates the framing that seven in ten CTOs are deeply concerned, or losing sleep, over SaMD development.
Now that SaMD has become a strategic necessity, many CTOs step forward with confidence, only to realize that what seems simple at first quickly becomes far more complex.
The Illusion of Simplicity: Why SaMD Feels Manageable, Until It Isn’t
Building medical device software often starts with a prototype or proof of concept. It looks simple: a few APIs, a mobile interface, a cloud database.
But here’s what many teams miss:
- Medical-grade software requires heavy documentation
- Design controls and traceability are not optional
- Validation and compliance are required before launch
- Post-market surveillance and update planning are a must
What seemed like a few months of development turns into years of iteration, delays, recertifications, and risk management issues. This is where CTOs begin to feel the heat.
Once that initial illusion fades, the deeper challenges begin to surface. These are the real operational and regulatory pain points that disrupt progress and keep CTOs awake at night.
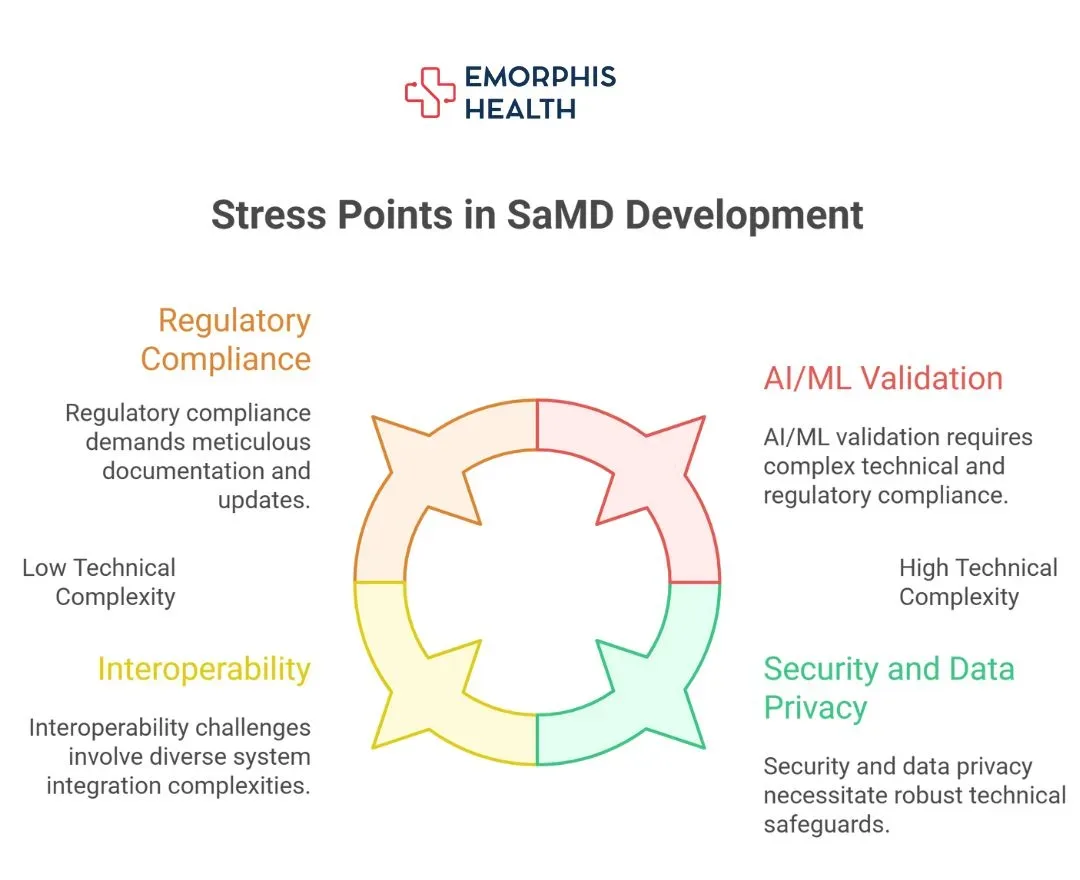
The Real Pain Points Keeping CTOs Up at Night
Let’s break down what’s creating stress for CTOs leading SaMD development:
a. Regulatory Flux and Global Compliance Overwhelm
Each region has its own rules:
- FDA requires Pre-market submissions and SaMD risk classifications
- EU MDR demands Clinical Evaluation Reports, UDI, and CE marks
- IEC 62304 adds software lifecycle expectations
Even worse? These rules keep changing. Staying compliant across regions requires constant updates to documentation, processes, and testing.
b. Interoperability Headaches and EHR Chaos
Every hospital or provider uses a different system: Epic, Cerner, Allscripts, or even homegrown solutions.
- Some expose APIs
- Others rely on HL7 or FHIR
- Many still need custom middleware or HL7 engines
SaMD needs to connect securely and seamlessly with these systems, and that’s where most teams hit a wall. Interoperability isn’t just a technical challenge—it’s a business risk if not solved early.
c. Security, Data Privacy, and Cloud Exposure
As soon as your SaMD stores or transmits patient data, you’re accountable for:
- HIPAA or GDPR compliance
- Data encryption in transit and at rest
- Secure cloud architecture
- Cyberattack prevention
Many teams underestimate this. A simple misconfiguration on AWS or Azure can lead to massive data breaches and legal trouble.
d. AI/ML Features: Excitement Meets Uncertainty
Many CTOs want to embed AI/ML into their SaMD for image analysis, predictive alerts, or personalization. But there are serious challenges:
- How do you validate a learning model?
- Can the FDA trust your black-box predictions?
- How often can the model update before you need re-certification?
It’s easy to add a model. It’s hard to prove it’s safe, reliable, and explainable.
e. The Testing Gap: When “It Works” Isn’t Enough
Unlike normal apps, SaMD needs:
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- Verification & validation (V&V)
- Clinical evaluation
- Usability testing under IEC 62366
- Real-world scenario testing
And all of this needs to be documented in a traceable, auditable manner. Miss a step, and regulators can stop your launch.

Faced with these growing challenges, many teams fall into a common trap: the decision between building in-house or buying from outside often looks clear-cut, but rarely is.
The Build vs Buy Trap in SaMD Decisions
Many companies think: “We’ll build it ourselves—it’s just an app.” This works… until:
- Your team realizes they don’t know IEC 62304 or FDA QSR
- The MVP fails usability testing
- Engineers can’t trace software changes to risk controls
- Documentation becomes an afterthought
Outsourcing sounds like the answer, but most vendors don’t understand medical regulations.
But even with the right platform or vendor, one harsh truth remains: without the right team and internal structure, execution breaks down fast.
Find the details for understanding healthcare compliance.
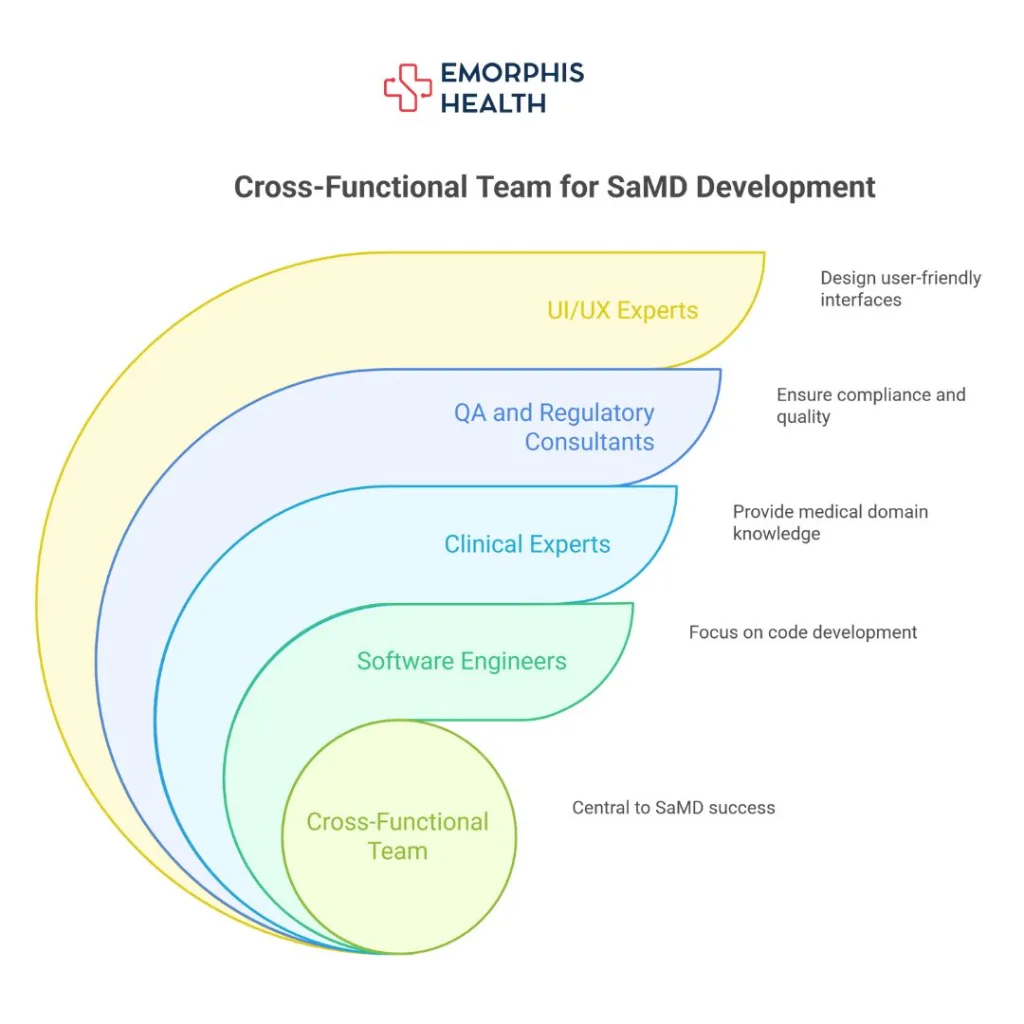
Talent and Team Structure: You Can’t Just Hire Your Way Out
Hiring one or two developers with “medical experience” isn’t enough. SaMD development requires a cross-functional team that includes:
- Software engineers
- Clinical subject matter experts
- Quality assurance and regulatory consultants
- Risk managers
- UI/UX experts in medical usability

Without the right team structure, communication breaks down. Engineers focus on code, not compliance. Product managers skip traceability. And when it’s time to file regulatory documents, you’re months behind.
Some CTOs, however, have found a way through. They are approaching SaMD with a mindset shift, one that balances speed, safety, and scale.
What the Smart CTOs Are Doing Differently
CTOs who succeed with Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) don’t treat it like any other software project. They understand that SaMD operates in a highly regulated environment where patient safety, compliance, traceability, and audit-readiness are just as important as product functionality.
These leaders aren’t just building software—they’re building the right ecosystem that allows SaMD to grow safely, quickly, and at scale.
Here’s how they approach it:
1. Design for Compliance from Day 1
Smart CTOs know that compliance isn’t something you “add later.” They start with regulatory standards in mind—right from the first design discussion.
They align product roadmaps with:
- IEC 62304 for medical software lifecycle management
- ISO 14971 for risk management throughout the product
- IEC 62366 for usability and human factors
- FDA and MDR guidelines for regulatory submissions and quality assurance
By doing this from the beginning, they avoid rework, ensure faster approvals, and reduce the risk of failing audits late in the process.
They treat compliance as a core design input, not a speed bump.
2. Use a Purpose-Built SaMD Architecture
Instead of building on generic mobile app stacks or retrofitting consumer platforms, successful CTOs invest in SaMD-specific architecture that supports:
- Modular development: So features can be added or updated without full re-certification
- Traceability: Linking requirements to risks, design controls, code, and tests
- Audit trails: For every code change, test result, and requirement update
- Security: Role-based access, secure data handling, and logging for PHI (Protected Health Information)
- Validation-ready workflows: That align with regulatory and quality frameworks
This architectural discipline gives them confidence not only in development but also in scaling, supporting updates, and passing audits globally.
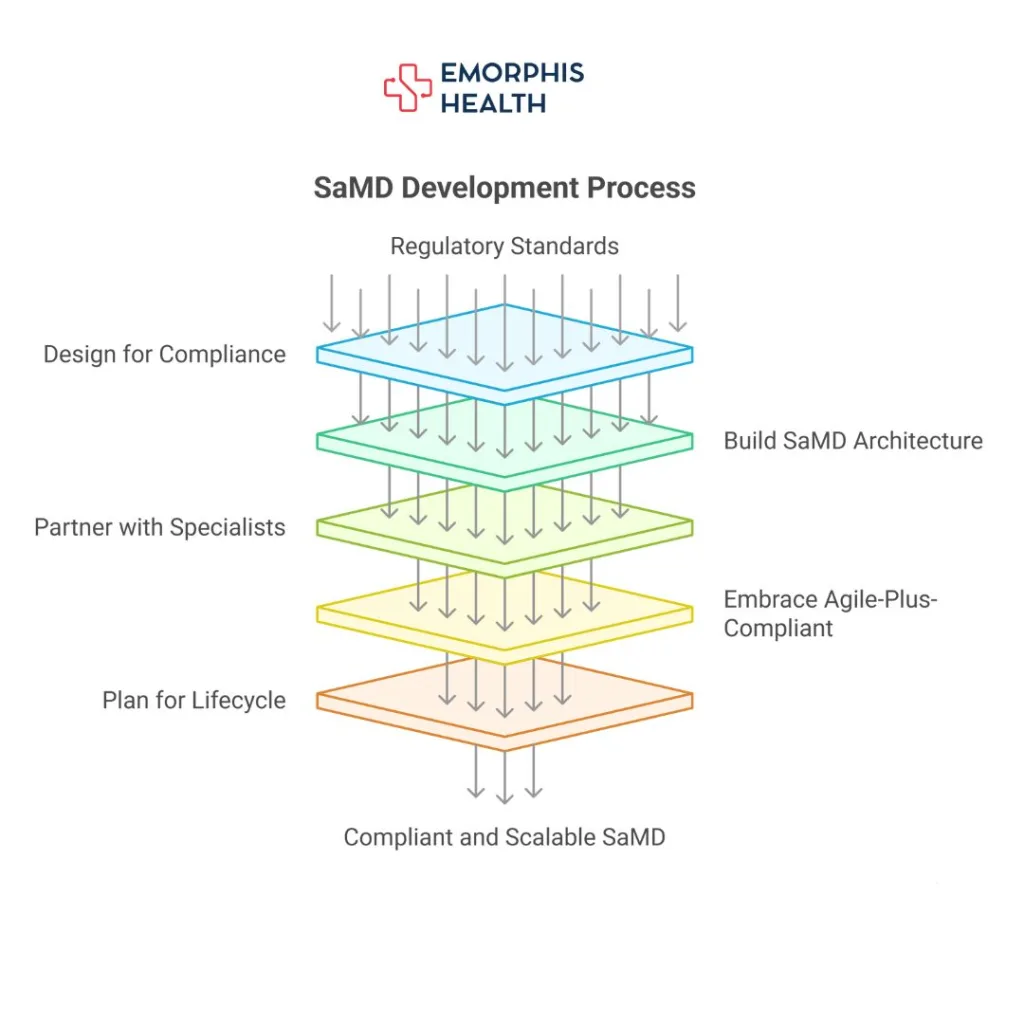

3. Work with Specialized Partners
They don’t hand SaMD to general-purpose app developers. They work with teams who know healthcare, know how to build for regulatory approval, and can map clinical needs to technical solutions.
These partners bring:
- Experience with regulatory audits and technical files
- Prebuilt accelerators like design history file templates
- Tools for risk traceability, usability validation, and verification
- Deep knowledge of how software and clinical workflows intersect
Find an expert guide on medical device software development.
4. Embrace Agile-Plus-Compliant
While many in the healthcare industry still use waterfall models for compliance, smart CTOs blend agile speed with regulatory discipline.
They adapt agile development to include:
- Formal documentation as part of each sprint
- Built-in checkpoints for risk analysis, traceability, and test coverage
- Incremental design control updates with every feature addition
- Ongoing review from regulatory, clinical, and QA experts—not just developers
This approach allows them to:
- Respond quickly to user feedback or market needs
- Maintain development velocity
- Stay in sync with quality and compliance teams
It’s not just about sprinting fast; it’s about sprinting in the right direction, with every stakeholder on board.
5. Build for the Long Game
Instead of just focusing on getting a product out the door, smart CTOs think beyond the launch. They plan for the full lifecycle of their SaMD:
- Post-market surveillance to track performance and real-world safety
- Update strategies that avoid triggering full re-certification
- Infrastructure for version control, rollback, and patching
- Scalability planning for new markets (e.g., FDA to MDR, or vice versa)
- Customer support systems for incidents, feedback, and issue tracking
They also invest in continuous improvement: not just fixing bugs, but improving usability, reducing clinical risk, and adapting to new guidelines (like AI/ML policy updates or new cybersecurity mandates). These CTOs understand that the true cost of SaMD isn’t in launch—it’s in maintenance, updates, and keeping it compliant for years.
This mindset is not just about technical decisions. It reflects a bigger picture. Because in the end, SaMD is no longer just software; it is a long-term strategic move.
Conclusion: SaMD Isn’t Just Software. It’s Strategy
Too many CTOs fall into the trap of treating Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) like just another digital app. But SaMD is fundamentally different. It directly impacts patient safety, clinical workflows, and must navigate a complex web of global regulations. When it fails, it doesn’t simply crash. It can be pulled from the market, face regulatory penalties, or worse, put lives at risk.
On the other hand, when built with the right strategy, SaMD becomes a powerful growth lever. It opens up new revenue opportunities, improves care delivery, and sets your medical device apart in a highly competitive market.
The CTOs who succeed with SaMD understand this from the beginning. They do not just ship features. They build a strong foundation of compliance, scalability, and clinical value. These leaders are not just developing software. They are shaping the future of digital healthcare.
Contact Us for more details.







