The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a profound transformation, shifting from a reactive “sick care” model to a proactive “lifecare” approach. Central to this evolution is precision medicine, an innovative strategy that tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. By considering genetic makeup, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices, precision medicine aims to optimize health outcomes and redefine our health journeys.
Precision medicine, what does that mean?
See Contents
Precision medicine is a cutting-edge approach to healthcare that customizes treatments based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. Instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach, precision medicine analyzes individual differences to provide more effective and targeted therapies.
Precision medicine enables healthcare providers to predict more accurately which prevention and treatment strategies will be most effective for specific individuals.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) describes precision medicine as an approach that takes into account individual differences to guide medical decisions, practices, and products.
For example, in cancer treatment, doctors can use genetic testing to identify specific mutations in a tumor and prescribe medications that directly target those mutations, improving the chances of success while minimizing side effects. This strategy is revolutionizing fields like oncology, cardiology, and rare disease management, making healthcare more personalized and efficient.

The Shift from Sick Care to Lifecare
Traditional healthcare systems have predominantly operated on a reactive basis, addressing illnesses and symptoms as they arise. This “sick care” model often leads to generalized treatments that may not be effective for everyone and can result in unnecessary side effects or complications.
Precision medicine facilitates a shift towards “lifecare,” emphasizing prevention, early detection, and personalized intervention. By identifying individual risk factors and susceptibilities, healthcare can become more proactive, focusing on maintaining wellness rather than merely treating disease.
This approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also reduces adverse reactions by ensuring that medications and therapies are tailored to a patient’s genetic profile.
Additionally, it enables the development of targeted therapies for chronic diseases, improving long-term health outcomes. By integrating genomics, data analytics, and AI-driven insights, precision medicine is paving the way for a more efficient and cost-effective healthcare system.
With its ability to personalize treatment and enhance patient outcomes, precision medicine is transforming the healthcare landscape. Let’s explore its real-world applications across various medical fields, from oncology to rare disease management.
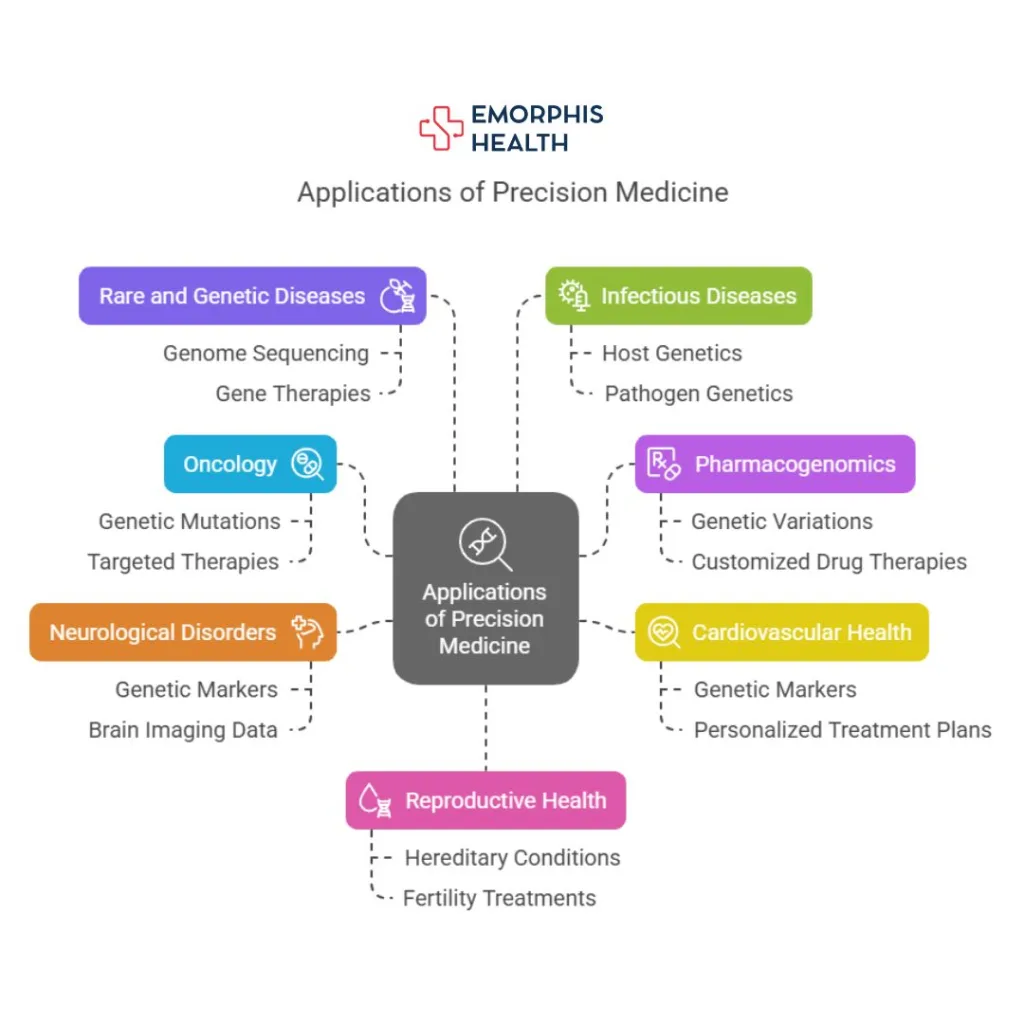
Applications of Precision Medicine
Precision medicine has already made significant strides in various medical fields:
- Oncology: Cancer treatment has been revolutionized by precision medicine. By analyzing the genetic mutations specific to a patient’s tumor, targeted therapies can be developed, improving treatment efficacy and reducing adverse effects.
- Pharmacogenomics: This field studies how genes affect an individual’s response to drugs. Understanding genetic variations allows for the customization of drug therapies, optimizing effectiveness, and minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
- Cardiovascular Health: Genetic and epigenetic markers are being used to predict cardiovascular disease risk, enabling early interventions and personalized treatment plans. For example, studies have developed more accurate equations for predicting cardiovascular risk by incorporating diverse factors such as genetics, socioeconomic status, and ethnicity.
- Neurological Disorders: Precision medicine is transforming the diagnosis and treatment of conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy. By analyzing genetic markers and brain imaging data, clinicians can identify disease risk earlier and tailor treatment plans to slow progression or manage symptoms more effectively.
- Rare and Genetic Diseases: Many rare diseases have a genetic basis, making them ideal candidates for precision medicine. Advances in genome sequencing help identify mutations responsible for these conditions, enabling the development of gene therapies and personalized treatment approaches.
- Infectious Diseases: Precision medicine is being applied to infectious disease management by analyzing host and pathogen genetics. This allows for more targeted treatments, optimized vaccine development, and personalized antimicrobial therapies, improving outcomes in conditions like HIV and COVID-19.
- Reproductive Health: Genetic testing enhances reproductive medicine by identifying potential hereditary conditions, guiding fertility treatments, and enabling personalized prenatal and neonatal care, ensuring better maternal and infant health outcomes.

The rapid advancements in technology are the backbone of precision medicine, enabling more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatments. Let’s explore the key technological innovations driving this transformative approach in healthcare.
Technological Innovations Driving Precision Medicine
Advancements in technology have been pivotal in the rise of precision medicine:
Genomic Sequencing
Genomic sequencing technology allows doctors to decode an individual’s entire genetic blueprint. This process involves analyzing DNA to identify specific genes, mutations, and variations that could affect how a person responds to diseases, treatments, and medications. As the cost of sequencing has significantly decreased, it’s become more accessible for routine use in healthcare. By understanding a patient’s unique genetic profile, doctors can provide highly targeted treatments that are more effective and have fewer side effects. For example, in cancer treatment, genomic sequencing can reveal mutations in cancer cells, allowing for the development of targeted therapies that attack the cancer more precisely, while sparing healthy tissue.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way healthcare providers make decisions. By analyzing vast amounts of medical data, AI can detect patterns that are too complex for the human eye. It can process everything from genetic information and medical histories to lab results and imaging scans, all in real-time. This enables the creation of highly personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s unique needs. AI is also revolutionizing clinical trials by helping to identify the right candidates for new treatments, ensuring that the right therapies are tested on the right patient populations. For instance, AI-powered tools can predict how a patient’s cancer might respond to different drugs, enabling doctors to select the most promising treatment options with greater confidence.
Wearable Technology and Remote Monitoring
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and health-tracking gadgets, are increasingly being used to monitor patients’ health in real-time. These devices can track a wide variety of health metrics, including heart rate, blood oxygen levels, physical activity, sleep patterns, and even blood sugar levels. This continuous flow of data allows healthcare providers to monitor their patients outside of the clinic and catch early signs of potential issues before they become serious. For instance, a smartwatch can alert a patient and their doctor if there is an abnormal heart rate or irregularity, enabling prompt medical attention. Additionally, wearable devices can track the effectiveness of ongoing treatments and provide feedback, helping doctors adjust therapy in real time based on how the patient’s body is responding. This kind of personalized, ongoing monitoring is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
While technological advancements are driving the progress of precision medicine, there are several challenges and ethical considerations that must be addressed to ensure its responsible and equitable implementation.
Let’s dive into the key issues that healthcare providers, patients, and policymakers must navigate as precision medicine continues to evolve.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its promise, precision medicine faces several challenges:
- Data Privacy: The collection and storage of genetic and personal health data raises concerns about confidentiality and the potential misuse of information.
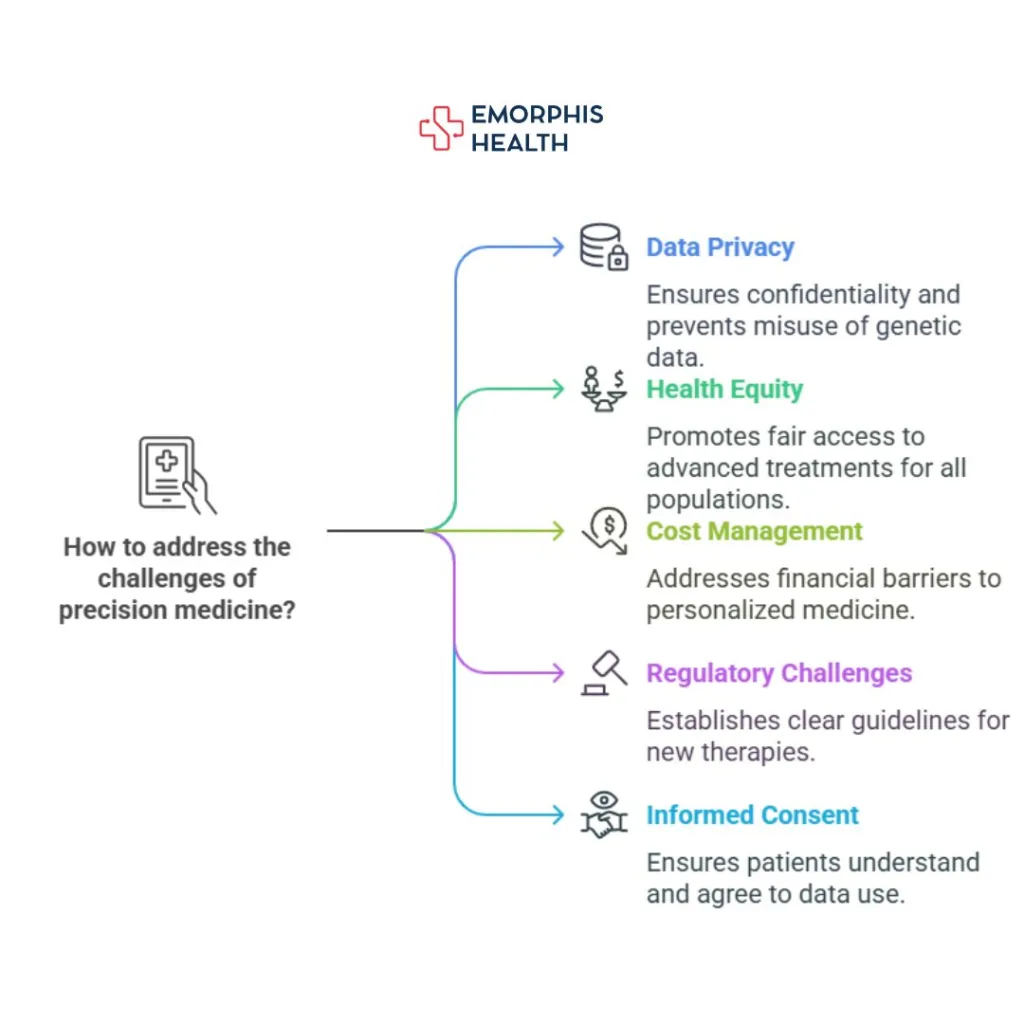

- Health Equity: There is a risk that precision medicine could exacerbate existing health disparities if access to advanced diagnostics and personalized treatments is limited to certain populations. Ensuring equitable access is crucial to prevent widening the healthcare gap.
- Cost: The development and implementation of personalized treatments can be expensive, posing challenges for healthcare systems and patients, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
- Regulatory Challenges: Precision medicine often involves new, innovative therapies and diagnostic tools that may not yet have clear regulatory frameworks. Ensuring that these new treatments are safe, effective, and properly regulated is a complex challenge for healthcare regulators worldwide. Developing robust regulatory processes that can keep pace with rapid innovation is key to ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy.
- Informed Consent: As precision medicine involves the collection of detailed genetic and personal health data, obtaining truly informed consent becomes more challenging. Patients must fully understand how their data will be used, who will have access to it, and the potential risks and benefits of participating in personalized treatments. Ensuring that consent is both transparent and fully understood is essential to maintaining trust in the healthcare system.
As we look toward the future, precision medicine holds immense potential to revolutionize healthcare further. However, overcoming the current challenges and addressing ethical concerns will be crucial in realizing its full benefits.
Let’s explore what lies ahead for precision medicine and how it could shape the future of healthcare.


The Future of Precision Medicine
Looking ahead, precision medicine is poised to further integrate into mainstream healthcare:
- Preventive Genomics: Routine genetic screening could become a standard part of preventive healthcare, identifying risks for various diseases and enabling early interventions. Studies have shown that genetic screening can significantly reduce premature deaths by identifying high-risk individuals early, allowing for targeted prevention strategies before diseases even develop.
- Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR hold the potential to correct genetic defects, offering cures for certain hereditary conditions. This groundbreaking advancement could not only treat diseases like cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia but also prevent the inheritance of genetic disorders in future generations, potentially eliminating certain diseases entirely.
- Global Collaborations: International initiatives, such as the NIH’s All of Us Research Program, aim to gather diverse health data to inform precision medicine approaches that are effective across different populations. By including a broad range of ethnicities, geographic locations, and healthcare systems, these collaborations ensure that precision medicine benefits are accessible to people worldwide, creating a more inclusive and equitable healthcare landscape.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: As AI and machine learning technologies evolve, they will become even more integrated into the development of precision medicine. These technologies will improve diagnostic accuracy, predict disease risks more precisely, and help design personalized treatment plans based on real-time patient data. AI can also help identify new biomarkers for diseases and provide insights into how genetic and environmental factors interact in complex ways.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell therapies and regenerative medicine could be combined with precision medicine to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. By using an individual’s own cells, this could offer highly personalized treatments that not only treat the disease but also regenerate and restore affected body parts, leading to longer-term health solutions.
- Expanded Access and Affordability: As technologies improve and scale, the cost of genetic testing, gene editing, and personalized therapies will likely decrease, making precision medicine more affordable and accessible to a larger portion of the global population. Efforts to make these advancements more affordable will be crucial for widespread adoption, particularly in developing countries.
- Precision Mental Health: The future of precision medicine isn’t just about physical health. Advancements in understanding the genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that contribute to mental health disorders could lead to highly personalized treatment plans for conditions like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. By tailoring psychiatric treatments to an individual’s genetic makeup, the effectiveness of therapies could be greatly improved.
The future of precision medicine is incredibly promising, with the potential to make healthcare not just reactive, but proactive, personalized, and ultimately more effective in treating and preventing diseases on a global scale.
Conclusion
The transition from a reactive sick care model to a proactive lifecare approach, driven by precision medicine, represents a significant advancement in healthcare. By focusing on the unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors of everyone, precision medicine offers the promise of more effective treatments, better health outcomes, and a more personalized healthcare experience. As technology continues to evolve and ethical challenges are addressed, precision medicine will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of healthcare, transforming how we prevent, diagnose, and treat disease.
As healthcare continues to evolve, the need for cutting-edge technology and innovative software solutions has never been more critical. At Emorphis, our team of healthtech experts is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of healthcare software product engineering. Whether you’re looking to develop personalized solutions or integrate the latest technological advancements, we offer the expertise needed to create impactful, scalable products that meet the ever-changing needs of the healthcare industry.
Connect with us to explore how our solutions can drive efficiency, improve patient outcomes, and support the future of healthcare innovation.







