Introduction
See Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Why is Patient Management System essential?
- 3 10 Key Features of a Patient Management System
- 4 Types of Patient Management Systems (PMS) in Healthcare
- 5 1. Based on Deployment Model
- 6 2. Based on Healthcare Facility Type
- 7 3. Based on Functionality and Use Case
- 8 4. Based on Patient Interaction and Engagement
- 9 5. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics and Decision Support Systems
- 10 How to Choose the Right Patient Management System
- 11 Get in Touch with Experts – Emorphis Health
- 12 Future Trends in Patient Management Systems
- 13 Conclusion
In the rapidly evolving world of healthcare, efficiency, accuracy, and seamless patient care have become top priorities. Healthcare providers constantly search for solutions that streamline administrative tasks while improving patient experience. This is where Patient Management Systems (PMS) come into play.
A Patient Management System is a digital platform that helps healthcare facilities manage patient information, appointments, medical records, billing, and communication efficiently. It acts as the backbone of modern healthcare practices, allowing clinics, hospitals, and healthcare providers to automate administrative tasks, enhance coordination, and improve patient outcomes.
Why is Patient Management System essential?
Traditional paper-based records and outdated management processes often lead to errors, inefficiencies, and poor patient experience. With a robust PMS, healthcare providers can:
- Reduce administrative burden by automating tasks like scheduling, record-keeping, and billing.
- Improve patient engagement by enabling seamless communication between doctors and patients.
- Ensure compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA (USA), GDPR (Europe), and HITECH Act.
- Enhance decision-making by providing real-time access to patient data for better diagnosis and treatment planning.
The adoption of Patient Management Systems is no longer optional but a necessity for healthcare providers looking to offer efficient, quality-driven, and patient-centered care.
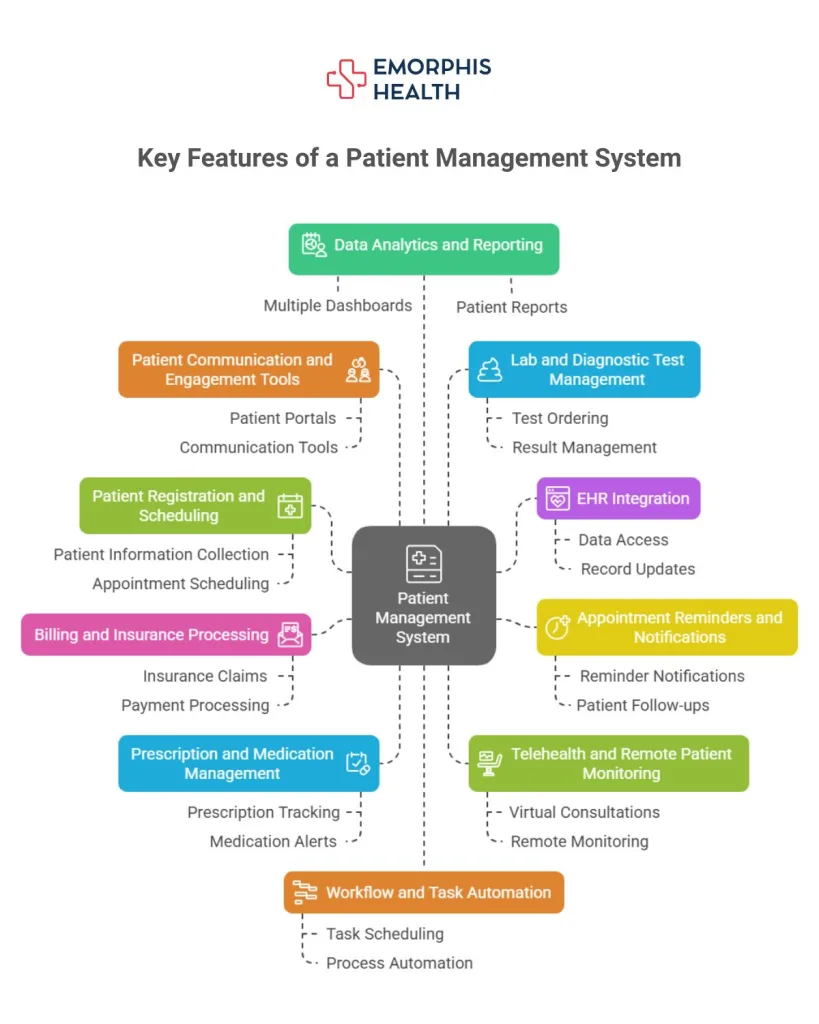
10 Key Features of a Patient Management System
A modern Patient Management System comes with various functionalities that cater to the needs of healthcare providers, patients, and administrators. Below are the key features:
1. Patient Registration and Scheduling
A PMS streamlines the patient registration process by allowing patients to self-register via an online portal or mobile app. This reduces administrative workload while improving accuracy. The system also automates appointment booking, rescheduling, and cancellations, helping healthcare providers optimize their schedules. By integrating appointment reminders and notifications, it minimizes no-shows and ensures that both doctors and patients stay informed about upcoming consultations.
2. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
Seamless integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) allows healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient information in real-time. This includes demographics, medical history, lab reports, prescriptions, and imaging results. A well-integrated PMS ensures better coordination among healthcare professionals, enabling data-driven decision-making. Moreover, it supports data privacy and security with encryption, access control, and compliance with global healthcare regulations.
3. Appointment Reminders and Notifications
A PMS plays a crucial role in reducing patient no-shows by sending automated reminders via SMS, email, or mobile apps. Patients can confirm, reschedule, or cancel their appointments effortlessly, ensuring better time management for healthcare professionals. Additionally, automated notifications help doctors and staff stay updated about upcoming consultations, reducing scheduling conflicts.
4. Billing and Insurance Processing
Managing finances efficiently is a vital aspect of any healthcare facility. A PMS automates billing, invoicing, and payment tracking, eliminating the need for manual data entry. It also streamlines insurance claim processing and verification, reducing delays in patient treatment. With multiple payment options integrated, including credit cards, digital wallets, and UPI, patients can make hassle-free payments while healthcare providers maintain accurate financial records.
5. Prescription and Medication Management
A robust PMS simplifies the prescription process by enabling healthcare providers to generate electronic prescriptions (e-prescriptions). These prescriptions can be directly shared with pharmacies, ensuring medication availability and reducing prescription errors. The system also sends medication reminders to patients, ensuring adherence to prescribed treatments. Additionally, it helps doctors identify potential drug interactions, minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
6. Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
The integration of telehealth features allows healthcare providers to offer virtual consultations via video conferencing. This is especially beneficial for remote areas where access to healthcare is limited. A PMS can also support remote monitoring for chronic disease management by integrating with IoT-based wearable devices that track patient vitals such as heart rate, glucose levels, and blood pressure. Secure doctor-patient communication through chat and telemedicine platforms enhances accessibility and ensures continuous care.
7. Patient Communication and Engagement Tools
A PMS enhances patient engagement by offering secure communication channels such as chat, email, and teleconsultation portals. It also provides a patient portal where individuals can access their medical records, lab results, and appointment history. Many advanced PMS solutions include AI-driven chatbots that answer patient queries, provide health tips, and guide users through their treatment plans.
8. Lab and Diagnostic Test Management
A PMS allows seamless integration with diagnostic labs and imaging centers, ensuring that test results are automatically updated in the patient’s records. This eliminates delays in retrieving test reports and reduces errors associated with manual data entry. Patients and doctors can access lab results instantly, enabling faster diagnosis and treatment.
9. Workflow and Task Automation
By automating administrative workflows, a PMS ensures smooth coordination between different departments in a healthcare facility. Tasks such as scheduling surgeries, managing patient admissions and discharges, and coordinating referrals are handled efficiently, reducing the workload on hospital staff. The system also tracks pending tasks and sends automated alerts to ensure no critical processes are missed.
10. Data Analytics and Reporting
A PMS provides real-time insights and reports that help healthcare providers make informed decisions. Hospitals can optimize their services and improve patient outcomes by analyzing patient demographics, treatment trends, financial performance, and operational efficiency. AI-driven analytics also enable predictive modeling, helping providers anticipate patient needs and resource requirements.

Now let’s look at the types of Patient Management System.
Types of Patient Management Systems (PMS) in Healthcare
A Patient Management System (PMS) is designed to improve healthcare efficiency by managing patient records, appointments, billing, and communication. However, not all PMS solutions are the same—different healthcare settings require different functionalities. Below are the main types of Patient Management Systems categorized based on their features, deployment models, and intended users.
1. Based on Deployment Model
a) On-Premise Patient Management System
An on-premise PMS is installed locally on hospital or clinic servers and managed by in-house IT teams. It provides full control over data security and customization but requires higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance. This type is preferred by large hospitals, multi-specialty clinics, and organizations with strict data compliance needs.
b) Cloud-Based Patient Management System
A cloud-based PMS is hosted on external servers and accessed via the internet. It offers scalability, remote accessibility, and reduced IT maintenance. This type is ideal for small to mid-sized clinics, telehealth providers, and healthcare institutions looking for cost-effective solutions.
2. Based on Healthcare Facility Type
a) Hospital Patient Management System
Designed for large hospitals and multi-specialty healthcare institutions, this system integrates with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), lab systems, radiology departments, and pharmacy management. It supports multi-location access, ensuring smooth coordination among departments and specialists.
Features:
- Bed management, surgery scheduling, and emergency response coordination.
- Advanced analytics for patient flow and hospital efficiency.
- Integration with medical equipment and lab diagnostics.
b) Clinic Patient Management System
A clinic PMS is tailored for independent doctors, small healthcare practices, and outpatient clinics. It focuses on appointment scheduling, patient records, and billing, ensuring streamlined administrative processes with minimal resources.
Features:
- Easy-to-use interface for doctors and staff.
- Quick appointment scheduling and prescription management.
- Integration with telemedicine platforms.
c) Dental Patient Management System
A dental PMS is customized for dental clinics, including treatment planning, X-ray image storage, and patient history tracking. It helps dentists manage appointments efficiently and track treatments for orthodontic, cosmetic, and restorative procedures.
Features:
- Dental charting and imaging.
- Automated appointment and follow-up reminders.
- Billing and insurance claim processing specific to dental care.
d) Mental Health and Therapy Management System
A PMS for mental health professionals is tailored for psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists, offering features like secure telehealth consultations, therapy session notes, and mood tracking for patients.
Features:
- HIPAA-compliant teletherapy integration.
- Patient mood tracking and therapy progress reports.
- Secure messaging and follow-up reminders.
3. Based on Functionality and Use Case
a) Appointment Scheduling and Patient Flow Management System
This system is focused on automating appointment scheduling, reducing patient wait times, and improving overall clinic efficiency. It is widely used in outpatient clinics and diagnostic centers.
Features:
- Online appointment booking and rescheduling.
- Queue management for reduced patient waiting times.
- Automated SMS and email reminders.
b) Integrated Patient Management and Electronic Health Records (EHR) System
A PMS with EHR integration is a comprehensive solution that connects patient records, lab reports, and treatment histories in one system. It is used by hospitals, multi-specialty clinics, and telehealth providers for efficient data management.
Features:
- Real-time access to patient medical history.
- Secure sharing of health records across different healthcare providers.
- Decision support tools for better treatment planning.
c) Patient Billing and Insurance Management System
This system is designed to handle medical billing, insurance claim processing, and financial reporting. It is essential for hospitals, private clinics, and insurance companies.
Features:
- Automated billing and invoicing.
- Insurance claim verification and processing.
- Payment gateway integration for online payments.
d) Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring System
With the rise of telehealth services, PMS solutions now include virtual consultations, remote health monitoring, and AI-driven health assistants. These systems are used by telemedicine providers, chronic disease management programs, and rural healthcare facilities.
Features:
- Video consultations and secure patient messaging.
- Integration with wearable health devices for real-time vitals tracking.
- AI-powered chatbots for basic patient queries and symptom checks.
4. Based on Patient Interaction and Engagement
a) Self-Service Patient Portals
A patient-facing PMS allows users to schedule appointments, view test results, pay bills, and communicate with healthcare providers through an online portal or mobile app. It is used by hospitals, multi-specialty clinics, and wellness centers to improve patient engagement.
Features:
- Secure access to medical records.
- Online prescription refills and teleconsultation options.
- AI-based health education and chat support.
b) AI-Driven Chatbots and Virtual Health Assistants
Some modern PMS solutions include AI-powered assistants that help patients book appointments, receive medication reminders, and get preliminary health guidance. These systems are used by telehealth platforms, hospitals, and healthcare startups.
Features:
- 24/7 virtual health assistance.
- Automated symptom assessment and triage.
- Integration with EHR for personalized recommendations.
5. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics and Decision Support Systems
An advanced type of Patient Management System integrates Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to analyze patient data, predict health risks, and assist healthcare providers in making data-driven decisions. These systems are widely used in hospitals, research institutions, and chronic disease management programs.
Features:
- AI-driven risk assessment and early disease detection based on patient history.
- Predictive analytics for readmission rates, patient deterioration, and treatment outcomes.
- Clinical decision support tools for personalized treatment recommendations.
- Automated alerts for medication adherence, abnormal vitals, and emergencies.
With AI integration, PMS solutions are not just administrative tools but intelligent healthcare assistants, ensuring proactive, personalized, and efficient patient care.
So, how to choose one of them, which suites you better, let us take a look.
How to Choose the Right Patient Management System
Selecting the right Patient Management System (PMS) is crucial for enhancing healthcare efficiency, improving patient experiences, and streamlining administrative workflows. With numerous options available, choosing the best one can be overwhelming. To help healthcare providers make an informed decision, here are key factors to consider when selecting a PMS.
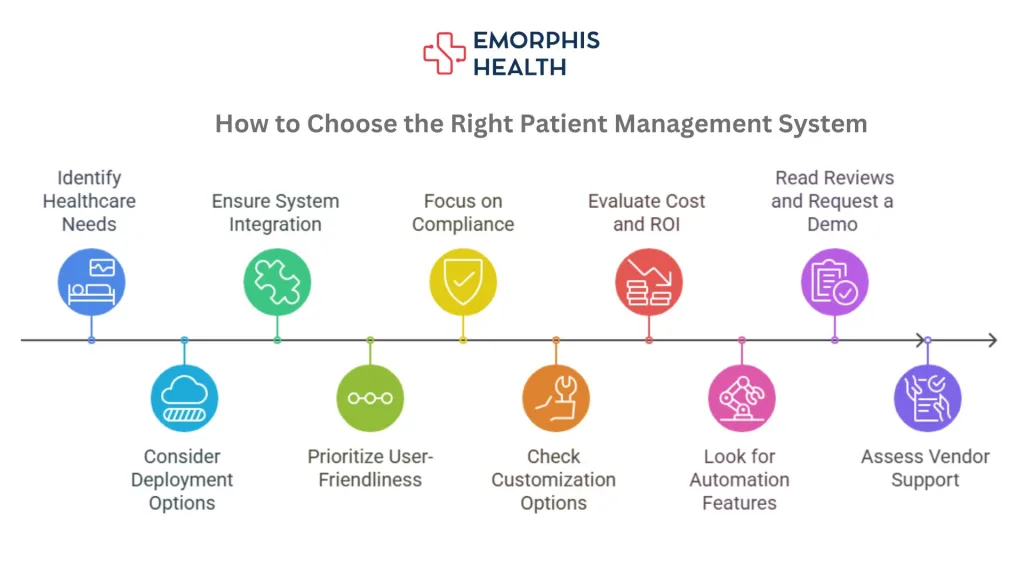

i. Identify Your Healthcare Facility’s Needs
Before choosing a PMS, it’s essential to understand your facility’s specific requirements. Consider factors such as:
- Size of the practice – Is it a small clinic, multi-specialty hospital, or telehealth provider?
- Number of patients handled daily – Does the system need to support high patient volumes?
- Integration needs – Does it require integration with EHR, billing, pharmacy, or laboratory systems?
- Compliance requirements – Must adhere to regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or HITECH Act.
By outlining your facility’s needs, you can narrow down solutions that align with your goals.
ii. Consider Deployment Options: Cloud vs. On-Premise
A PMS can be either cloud-based or on-premise, and selecting the right deployment model depends on budget, security concerns, and operational flexibility.
-
Cloud-Based PMS
- Accessible from anywhere via the internet.
- Lower upfront costs, with a subscription-based model.
- Automatic updates and scalability.
- Best for small to mid-sized clinics and telehealth services.
-
On-Premise PMS
- Hosted on local servers, providing greater control over data security.
- High initial investment but customizable.
- Requires in-house IT support for maintenance.
- Ideal for large hospitals and institutions with strict compliance needs.
If remote accessibility and scalability are priorities, cloud-based PMS is the better option. For strict data control, an on-premise solution is recommended.
iii. Ensure Seamless Integration with Existing Systems
A PMS should work seamlessly with other healthcare software such as:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) for unified patient data access.
- Billing & Insurance Management Systems to handle claims and payments.
- Telemedicine Platforms for virtual consultations.
- Pharmacy & Lab Management Systems for prescription and diagnostic data.
Check if the PMS supports HL7 and FHIR standards for interoperability, ensuring efficient data exchange between systems.
iv. Prioritize User-Friendliness and Ease of Adoption
A complicated PMS can slow down operations and frustrate healthcare providers. Choose a system with:
- Intuitive dashboards for quick navigation.
- Minimal learning curve for easy adoption by doctors and staff.
- Mobile accessibility for patient records on the go.
- Role-based access to control user permissions.
A system with comprehensive training and customer support ensures smooth implementation.
v. Focus on Compliance and Data Security
Since healthcare deals with sensitive patient data, the PMS must comply with global security and privacy regulations such as:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe.
- HITECH Act for secure electronic health information sharing.
Features like data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and automated backups enhance security and protect patient privacy.
vi. Check Customization and Scalability Options
Your healthcare facility may expand in the future, requiring a scalable PMS that can:
- Handle growing patient volumes.
- Adapt to new specialties and services.
- Support multi-location facilities.
- Integrate emerging technologies like AI and IoT.
Additionally, look for a PMS that allows customization, enabling providers to modify workflows, reports, and templates according to specific needs.
vii. Evaluate Cost and ROI
The cost of a PMS varies based on features, deployment model, and licensing fees. Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), including:
- Upfront costs for software installation or setup.
- Subscription fees for cloud-based solutions.
- Maintenance and upgrade expenses.
- Training and support costs.
While budget is important, focus on the ROI (Return on Investment)—a well-chosen PMS will improve efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and enhance patient care, making it a valuable long-term investment.
viii. Look for Automation and AI-Powered Features
Modern PMS solutions leverage automation and AI to optimize healthcare workflows:
- Automated appointment scheduling and reminders reduce no-shows.
- AI-powered chatbots enhance patient engagement.
- Predictive analytics assist in identifying at-risk patients.
- Voice recognition simplifies doctor-patient interactions.
Choosing a PMS with automation features can increase efficiency and save time for healthcare professionals.
ix. Read Reviews and Request a Demo
Before finalizing a PMS, research reviews from other healthcare providers and check for:
- Customer satisfaction and usability feedback.
- Response time for technical support.
- System uptime and reliability reports.
Request a free trial or demo to test the system’s functionality before making a purchase.
x. Assess Vendor Support and Training Services
A PMS is only as good as the vendor support behind it. Look for:
- 24/7 customer support for troubleshooting.
- Training programs for doctors, nurses, and administrative staff.
- Regular updates to keep the system up-to-date with healthcare trends.
A responsive vendor ensures long-term reliability and seamless operations.


Get in Touch with Experts – Emorphis Health
Choosing the right Patient Management System can be a game-changer for your healthcare practice, but navigating the vast array of options requires expert guidance. At Emorphis Health, we specialize in cutting-edge healthcare software solutions, ensuring seamless patient management, interoperability, security, and automation. Whether you’re looking for custom PMS development, AI-driven analytics, telehealth integration, or cloud-based solutions, our team of experts is here to help.
Connect with us today to explore how Emorphis Health can transform your healthcare operations with innovative, scalable, and future-ready technology. Let’s build smarter healthcare together.
Future Trends in Patient Management Systems
The Patient Management System (PMS) landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, automation, data analytics, and patient-centric innovations. As healthcare providers strive to enhance efficiency, improve patient experiences, and streamline operations, several key trends are shaping the future of PMS.
a. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming PMS by enabling predictive analytics, automation, and decision support. With AI, healthcare providers can:
- Predict patient health risks based on historical data.
- Automate appointment scheduling, billing, and insurance claims processing.
- Use chatbots and virtual assistants for 24/7 patient support.
- Leverage AI-driven clinical decision support systems (CDSS) to recommend treatment plans.
AI-driven PMS will help reduce administrative burden, enhance efficiency, and improve clinical outcomes.
b. Telehealth Integration for Remote Patient Monitoring
The rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring (RPM) is making PMS more accessible and versatile. Future-ready PMS solutions will integrate with:
- Wearable devices to track vitals like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels.
- Smart home healthcare tools for monitoring chronic conditions.
- Video consultation platforms to connect doctors and patients seamlessly.
This integration will bridge the gap between in-person and virtual healthcare, improving accessibility and continuity of care.
c. Interoperability and Unified Health Data Exchange
A major challenge in healthcare is fragmented data across multiple systems. Future PMS solutions will prioritize interoperability, ensuring seamless data exchange between:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
- Laboratory Information Systems (LIS)
- Pharmacy and Imaging Systems
- Health Information Exchange (HIE) Networks
Standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7 will drive this transformation, allowing real-time data sharing across healthcare networks.
d. Cloud-Based and Mobile-First PMS Solutions
The shift toward cloud computing and mobile-friendly PMS platforms will continue to grow, offering:
- Anytime, anywhere access for healthcare professionals and patients.
- Lower infrastructure costs compared to traditional on-premise solutions.
- Enhanced data security and automated backups.
A mobile-first PMS will enable doctors to access patient records, update charts, and communicate with patients on the go, improving workflow efficiency.
e. Blockchain for Secure and Transparent Healthcare Data
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in PMS for secure, transparent, and immutable health record management. With blockchain, PMS can:
- Enhance data security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Facilitate secure patient consent management.
- Enable decentralized health data sharing without intermediaries.
As data privacy regulations like HIPAA and GDPR tighten, blockchain-driven PMS will play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and patient data protection.
f. Personalized and Patient-Centric Care
The future of PMS is shifting towards personalized healthcare, where systems:
- Analyze patient behavior and preferences to offer customized treatment plans.
- Provide personalized health recommendations based on AI-driven insights.
- Use patient engagement tools like self-service portals, chatbots, and digital wellness programs.
By empowering patients with more control over their health data, PMS will enhance patient satisfaction and treatment adherence.
g. Voice-Activated and Natural Language Processing (NLP) Features
Voice technology and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are making PMS more intuitive and user-friendly. Future advancements include:
- Voice-assisted charting, allowing doctors to dictate patient notes hands-free.
- AI-driven transcription to reduce manual data entry.
- Conversational AI for patient engagement, improving communication and follow-ups.
These innovations will save time, improve accuracy, and reduce burnout among healthcare providers.
h. IoT and Smart Medical Device Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing patient care and management by integrating PMS with:
- Smart wearables for real-time health monitoring.
- AI-powered diagnostic tools for early disease detection.
- Remote monitoring solutions for chronic disease management.
With IoT-driven PMS, healthcare providers can track real-time patient data, enabling proactive and preventive care.
i. Data-Driven Insights for Value-Based Care
Healthcare is shifting towards value-based care models, where data analytics plays a crucial role. Future PMS solutions will:
- Provide advanced reporting and analytics to assess patient outcomes.
- Use machine learning to identify trends in treatment effectiveness.
- Help healthcare organizations move from fee-for-service to outcome-based payment models.
This shift will enhance care quality while optimizing healthcare costs.
j. AR & VR in Patient Engagement and Medical Training
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are emerging as powerful tools in healthcare, enhancing:
- Patient education by providing immersive 3D models of medical conditions.
- Virtual training for healthcare professionals, improving skills and efficiency.
- Rehabilitation therapy, helping patients recover faster through interactive exercises.
Future PMS will integrate AR/VR tools to enhance both clinical workflows and patient experiences.
Conclusion
A Patient Management System (PMS) is no longer just an administrative tool—it is the backbone of modern healthcare operations. From streamlining patient records and automating workflows to enhancing telehealth capabilities and leveraging AI-driven insights, PMS solutions are transforming the way healthcare providers deliver, manage, and optimize patient care. As technology continues to evolve, the future of PMS will be defined by interoperability, predictive analytics, IoT integration, and patient-centric innovations. Investing in the right PMS not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances patient experiences and health outcomes. Now is the time for healthcare organizations to embrace smart, scalable, and future-ready PMS solutions to stay ahead in an increasingly digital and data-driven healthcare ecosystem.