Overview
See Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Myth 1. AI Will Replace Healthcare Professionals
- 3 Myth 2. AI Works Without Human Intervention
- 4 Myth 3. AI is Only Beneficial for Large Hospitals and Research Centers
- 5 Myth 4. AI Has No Bias and is Completely Objective
- 6 Myth 5. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare is Too Costly for Widespread Use
- 7 Myth 6. AI Threatens Patient Privacy and Data Security
- 8 Myth 7. AI Can Diagnose Diseases on its Own
- 9 Myth 8. AI is a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
- 10 Conclusion: Moving Beyond Misconceptions for a Smarter AI Future in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming healthcare in ways previously unimaginable. From supporting diagnostics to streamlining patient management. Before we dive into exploring some of the common misconceptions about artificial intelligence in healthcare, let’s take a look at some recent statistics on how artificial intelligence in healthcare is growing.
A recent report from Maximize Market Research estimates that artificial intelligence in the healthcare market was worth $19.68 billion in 2023. This market is expected to expand significantly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.57% projected from 2024 through 2030, reaching nearly $183.56 billion by the end of that period.
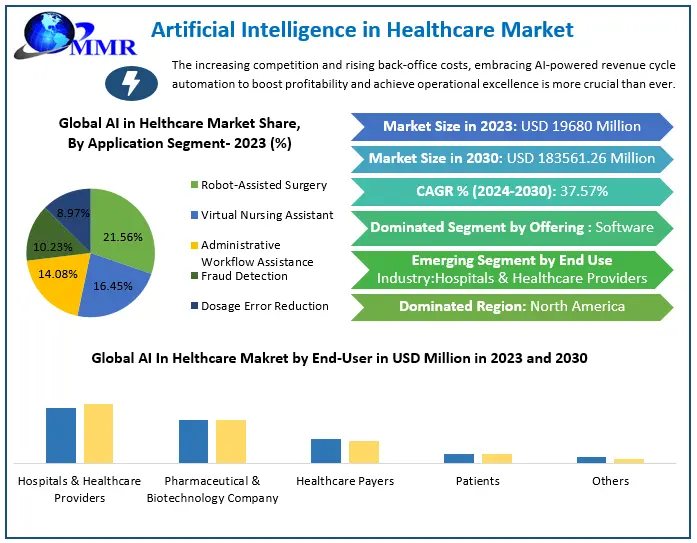
Canada stands out as a leader in adopting AI within its healthcare sector, largely due to its robust healthcare infrastructure and strong analytics network. Research by MMR Research indicates that the Canadian AI healthcare market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 34%, with an even more impressive average annual growth rate of 55% from 2023 to 2030.

Globally, automated report generation is gaining traction, driven by advancements in IT and the growing availability of remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions. RPM, in particular, enhances clinical assessments, supports decision-making accuracy, and reduces hospitalization risks. The demand for RPM services is rising as a response to the prevalence of conditions like cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. As the aging global population seeks healthier lifestyles, RPM use is anticipated to grow further. Expanding telemedicine also requires collaborative efforts from governments and insurers to create sustainable reimbursement models that support a wide range of patient needs.
Grand View Research reports that the global market for artificial intelligence in healthcare was valued at approximately $19.27 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.5% from 2024 to 2030. This rapid expansion is largely driven by the growing demand for greater efficiency, precision, and improved patient outcomes within the healthcare sector.
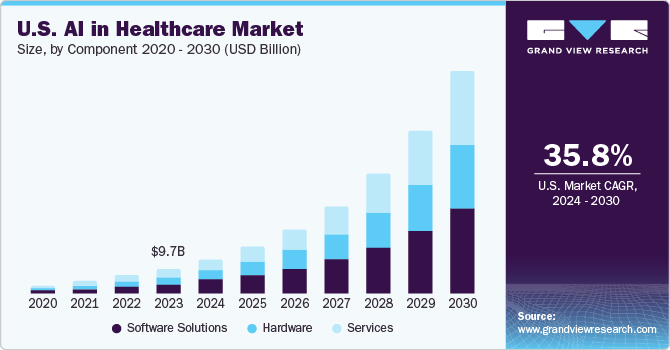
In the same report, it’s mentioned that a Microsoft-IDC study conducted in March 2024, in the same, 79% of healthcare organizations are currently employing AI technology. Additionally, AI investments are delivering a strong return, with an ROI of $3.20 for every $1 spent, typically realized within 14 months. AI’s potential to revolutionize areas such as medical imaging analysis, predictive analytics, personalized treatment planning, and drug discovery could significantly reshape traditional healthcare practices.
As reported by Statista, the global market for artificial intelligence in healthcare was valued at over $11 billion in 2021, with projections suggesting it could grow to approximately $188 billion by 2030.
A survey conducted in the United States identified security and privacy threats as the primary concern regarding the growing use of artificial intelligence in healthcare. Additional ethical worries included safety risks and the possibility of AI being exploited by malicious actors. In Europe, a separate survey revealed that patients were more inclined to trust AI when it was used alongside expert judgment, rather than relying on AI to make decisions independently. While some potential patients share these concerns, a majority of healthcare executives believe that investing in AI will enhance both health outcomes and the overall patient experience in hospitals and healthcare facilities.
AI is heralding a new era of efficient healthcare delivery. However, many misconceptions about AI are hindering its full adoption. Some fear it will replace healthcare professionals, while others worry about privacy and the financial impact of implementation.
Lets take a look on the most common misconceptions about artificial intelligence in healthcare to clarify what AI can realistically offer—and what it cannot.
Myth 1. AI Will Replace Healthcare Professionals
One of the most prevalent misconceptions about AI is that it will eventually replace healthcare professionals. While AI can enhance decision-making, it doesn’t substitute human judgment or expertise. AI algorithms can quickly analyze data patterns and suggest possible diagnoses or treatment options, but these are ultimately recommendations, not final judgments. For instance, a machine learning model might flag abnormalities in imaging scans, but it is still up to a radiologist or doctor to interpret the results and decide on the next steps. AI acts as a helpful tool, not a replacement, and works best as an assistant to trained healthcare professionals.
Myth 2. AI Works Without Human Intervention
Another misconception about AI is that it operates autonomously, requiring no human oversight. In reality, AI models in healthcare are only effective when continuously monitored and adjusted by human experts. Machine learning models, for example, need to be trained on data that reflect the real-world healthcare context. Furthermore, because healthcare is so nuanced and personal, AI outcomes are more reliable when checked by healthcare providers who can apply a clinical perspective to its findings.
For instance, an AI model could be trained to identify signs of a certain condition based on historical data. However, without expert validation, there is a risk that the model could miss new or unusual symptoms not covered in its training data. Human intervention ensures that AI tools are applied with appropriate caution and remain aligned with clinical objectives.
Myth 3. AI is Only Beneficial for Large Hospitals and Research Centers
There’s a common belief that AI solutions are only accessible to large hospitals and research centers, leading to another misconception about artificial intelligence in healthcare. Many assume smaller clinics and rural healthcare providers cannot benefit from AI because of the perceived cost or complexity. However, AI technologies today are designed to be adaptable for a variety of settings, including smaller facilities.
For instance, AI tools can assist rural healthcare providers by offering diagnostic support through telehealth systems, allowing specialists in urban centers to review and diagnose cases remotely. In this way, even smaller practices can leverage AI to offer higher-quality care to patients, often at a reasonable cost.
Myth 4. AI Has No Bias and is Completely Objective
One of the misconceptions about AI that needs urgent attention is the belief that AI is completely objective and free from bias. While AI has the potential to reduce some forms of bias, it can also inadvertently reinforce existing biases if trained on unbalanced data. For instance, if an AI model is trained on data that doesn’t represent a diverse patient population, its predictions might be less accurate for underrepresented groups.
In healthcare, this bias can manifest in critical areas like diagnostics and treatment recommendations. To mitigate this, healthcare AI systems need data that represents diverse populations, and continuous evaluation is necessary to identify and correct biases. Healthcare professionals play a key role in validating AI findings and ensuring they are inclusive and fair.
Myth 5. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare is Too Costly for Widespread Use
Another misconception about AI is that it’s prohibitively expensive, making it unfeasible for widespread adoption. While AI systems can require an initial investment, many are designed to deliver long-term value by reducing manual workloads, improving accuracy, and enhancing patient outcomes. AI tools can streamline administrative tasks, freeing up healthcare providers to focus more on patient care, which can actually result in cost savings over time.
For example, AI can help automate patient data entry or predict patient volumes, which allows healthcare facilities to allocate resources more efficiently. Over time, the improved efficiency and reduced overhead can offset the initial investment, making AI a financially viable option for many healthcare providers.
Myth 6. AI Threatens Patient Privacy and Data Security
Concerns around patient privacy and data security are widespread, leading to another misconception about AI. While AI requires access to large amounts of data, robust encryption, anonymization, and compliance with healthcare regulations (like HIPAA) are integral parts of its design. AI systems used in healthcare are often built with stringent security protocols to protect sensitive patient data.
For example, machine learning algorithms can be trained on anonymized data to ensure patient privacy is protected. With the right security measures in place, AI can be implemented without compromising data security, allowing healthcare providers to benefit from advanced insights while upholding strict patient confidentiality.
Myth 7. AI Can Diagnose Diseases on its Own
Another misconception about AI is that it can independently diagnose diseases. AI can indeed assist in identifying potential health conditions by analyzing symptoms or medical images, but it does not replace the expertise of healthcare providers. AI is meant to enhance diagnostic accuracy by offering initial insights, but the final diagnosis and treatment decisions are still made by physicians.
For instance, AI might detect patterns in scans that suggest the presence of a certain disease, but this does not equate to a diagnosis. The healthcare provider evaluates the AI-generated insights in the broader context of the patient’s history, symptoms, and other test results before reaching a conclusion. Thus, AI serves as a diagnostic aid rather than a standalone solution.
Myth 8. AI is a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
One persistent misconception about AI is that it works universally in any healthcare setting without customization. The truth is, healthcare environments are unique, with specific challenges and patient needs that require tailored AI solutions. What works in a large hospital may not be suitable for a smaller clinic or specialized practice.
For example, a general AI system designed for primary care might not meet the specific needs of an oncology department. Each setting requires an AI system that is aligned with its clinical objectives, data requirements, and operational workflows. Customization and adaptability are key for successful AI implementation in healthcare, allowing the technology to meet the unique needs of each provider and patient population.
Conclusion: Moving Beyond Misconceptions for a Smarter AI Future in Healthcare
By addressing these misconceptions about AI, healthcare providers and stakeholders can make more informed decisions about adopting AI technologies. Artificial intelligence in healthcare holds great potential, but it’s crucial to approach it with realistic expectations. As per various reports, we also conclude that the AI adoption is increasing. Far from replacing healthcare professionals, AI serves as a powerful tool to support their work. With responsible use, tailored implementations, and vigilant oversight, AI can help the healthcare industry tackle some of its most pressing challenges, enhancing care quality while respecting the unique needs of patients and providers alike.
In conclusion, as AI continues to revolutionize the healthcare industry, partnering with the right experts is crucial to harness its full potential. At Emorphis, our team of AI specialists is dedicated to delivering cutting-edge solutions that drive efficiency, accuracy, and improved patient outcomes. Whether you’re looking for AI software development or integration in medical imaging, predictive analytics, or personalized treatment planning, connecting with Emorphis experts ensures that your healthcare innovations are backed by robust, scalable, and impactful AI solutions.







